Assumption Management: Modern Solutions in a Complex World
I. Introduction
As the complexity of financial markets and regulatory environments continues to grow, life insurers are placing greater reliance on their behavioral, economic, and demographic assumptions to drive critical business decisions. Behavioral assumptions are essential in financial reporting, economic assumptions inform earnings forecasting, and demographic assumptions underpin product pricing. Collectively, these assumptions guide insurers in assessing the feasibility of entering new markets, determining the viability of transaction deals, and providing a clear explanation of earnings—particularly when explaining period-over-period changes due to updates in assumptions like mortality rates, lapse behavior, or economic outlooks. However, despite this heavy reliance, the maturity of assumption management practices varies widely across organizations, with many opportunities for enhancement.
Over the past decade, insurers have modernized many functions—shifting to cloud-based data platforms, automating financial reporting, and enhancing actuarial modeling systems. While some insurers have made strides towards improving their assumptions management through improved documentation and more formalized governance structures, the complexity of governing these diverse assumptions across products, functions, and models remains a challenge for many. This article examines the evolution of assumption management, persistent challenges, and how companies can strengthen their approach by thoughtfully deploying technology into their operating model.
II. The Persistent Challenges of Assumption Management
Assumption management encompasses a comprehensive set of practices including experience analysis, assumption development, structured governance processes, accurate implementation into actuarial models, and ongoing monitoring of assumption performance relative to experience. It requires more than a governance committee and a SharePoint folder—it demands an operating model inclusive of technology integrated with source-of-truth data and actuarial models to enable transparency, auditability, and analytics across actuarial, finance, and risk functions.
Many chief actuaries have thought, “I oversee multiple products, models, and reporting bases—yet I still find myself chasing down answers to questions about assumptions across multiple teams and spreadsheets. I just want everything in one place, and I want to trust it’s right.”
This sentiment conveys the frustration expressed by many insurance leaders dealing with their antiquated assumption-management practices. A modern framework should enable the following:
- Ongoing development of assumptions informed by a reliable and consistent source of experience data, thoughtfully integrating relevant external data where appropriate.
- Governed implementation of assumptions into models and tools in a controlled, auditable way—serving as a single source-of-truth across valuation, pricing, and forecasting.
- End-to-end traceability from reported results to underlying assumptions used.
- Consistency and harmonization of assumptions across business functions, product lines, and reporting frameworks.
Some companies have taken steps to improve assumption management through modeling modernization initiatives and enhancements to experience study processes. However, these efforts need to be made holistically rather than fragmented among specific models or functions. Without a holistic approach, improvements often fail to capture practical opportunities—such as greater efficiency, fewer errors, improved cross-team alignment, and clearer management insights.
III. A History of Incremental Progress: How Assumption Management Has Evolved
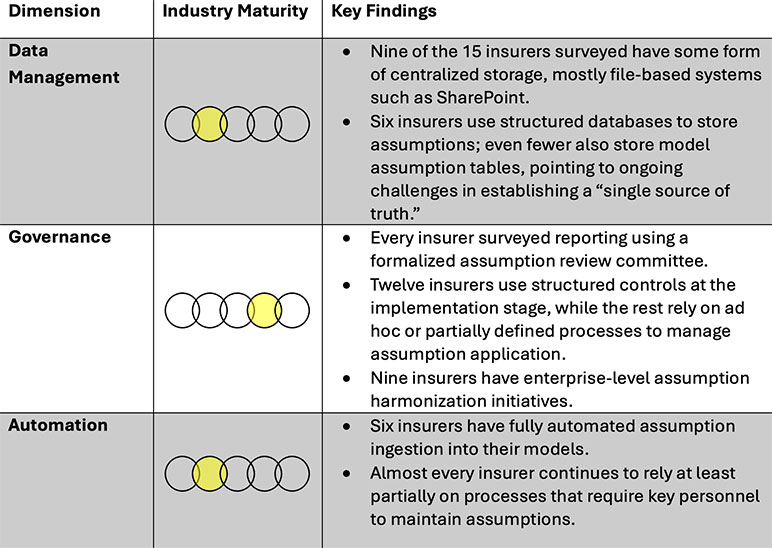
While assumption management has improved over time, progress has been slow and uneven. We recently surveyed 15 U.S. life insurers and found that despite some strides in enterprise assumption governance practices, many insurers still face challenges integrating and managing assumptions using a single, centralized, source-of-truth. (See Figure 1)
Figure 1
Survey Findings—Key Trends in Assumption Management
IV. Solution and Platform Considerations: Centralized Assumption Repositories
Different categories of assumptions—such as economic (e.g., interest rates), behavioral (e.g., lapse rates), and demographic (e.g., mortality rates)—may have distinct requirements for update frequency, granularity, sensitivity analysis, and governance. A well-designed centralized repository should accommodate these varying needs.
To address these challenges, companies are increasingly turning to centralized assumption repositories. A well-designed assumption repository plays a role in:
- A Single Source-of-Truth: Centralized storage ensures consistency and accessibility of actuarial assumptions across business functions.
- Automated Model Ingestion and Version Control: Reduces manual assumption handoffs by feeding assumptions directly into actuarial models through governed, versioned pipelines, eliminating errors and improving efficiency.
- Sensitivity Testing and Attribution Analysis: Enables downstream models to efficiently consume different assumption sets, supporting scenario analysis, attribution, and faster iteration without altering core data.
- Governance and Compliance: Provides built-in audit trails, clear versioning, and structured approval workflows directly within the repository, enhancing transparency and auditability of assumption changes.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Enables alignment among valuation, experience studies, pricing and other functional teams by improving assumption accessibility and documentation.
Achieving these outcomes requires thoughtful design and execution. The following are guiding principles that contribute to an effective assumption repository framework. (See Figure 2)
Figure 2
Guiding Principles for an Effective Assumption Repository
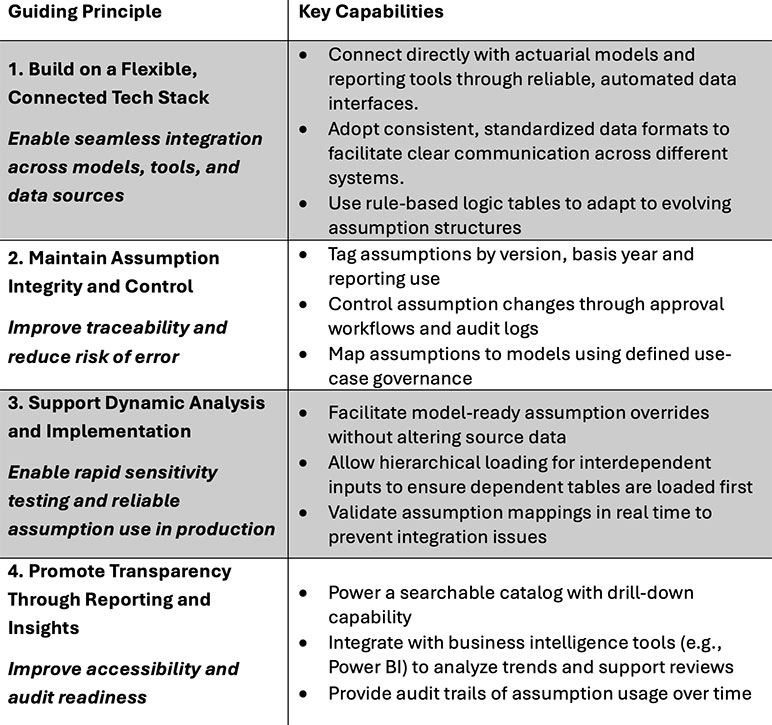
By aligning with these guiding principles, companies can build a scalable and robust centralized assumption repository that reduces inefficiencies, strengthens governance, and supports better decision-making across actuarial and financial functions.
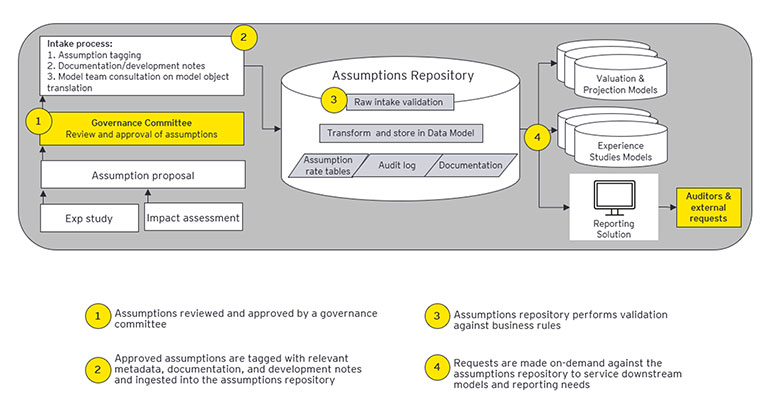
V. Architecture and Design Considerations
Incorporating the guiding principles for a centralized assumptions repository into a comprehensive solution introduces a number of design considerations. The architecture diagram (see Figure 3) reflects how these considerations come together, highlighting key components and capabilities that support a scalable, integrated assumption repository.
Figure 3
High-level Illustrative Assumption Management
VI. Conclusion: Moving Toward a More Sophisticated Assumption Management Solution
The transformation of assumption management is no longer just an efficiency play—it’s about enabling insurers to understand their business better, respond to changing market conditions more quickly, and have greater confidence in their actuarial analysis. When insurers have timely and reliable access to their underlying assumptions, they can more clearly identify drivers of risk and performance, helping them explain results internally and externally with greater transparency.
In a rapidly evolving market, insurers must periodically refine their assumptions about policyholder behaviors, economic outlooks, and demographics to remain competitive and responsive to new regulatory expectations. Centralizing, automating, and governing assumptions becomes essential for:
-
Improving the clarity of and confidence in internal and external communications.
-
Enhancing the ability to assess transactions, pricing, and capital decisions to keep pace with business demands.
-
Increasing agility in response to economic shifts or regulatory changes.
-
Freeing up actuarial and finance resources to focus on analysis rather than data wrangling, thereby unlocking faster, more reliable insights.
Many insurers have made meaningful progress, but assumption management often still lags behind other areas of transformation. The real question isn’t whether to modernize it, but rather how much value is being left on the table by not doing so. For those looking to elevate assumption management, the time is now.
This article is provided for informational and educational purposes only. Neither the Society of Actuaries nor the respective authors’ employers make any endorsement, representation or guarantee with regard to any content, and disclaim any liability in connection with the use or misuse of any information provided herein. This article should not be construed as professional or financial advice. Statements of fact and opinions expressed herein are those of the individual authors and are not necessarily those of the Society of Actuaries or the respective authors’ employers.

